To take advantage of Cast Shadows or Ambient Occlusion, it is helpful to have multiple Volume Objects or larger overall elevation ranges in the Surface Map. The size and value of both the Cast Shadow and the Ambient Occlusion are dependent on the relative elevations of the surface; the Cast Shadow also depends on the Light Position relative to the surface’s mapping.
-
Start by setting up a simple Surface Map node with two image sources. To do this, follow the steps in How to Rig with Surface Shading.
To create a Surface Map that combines multiple Volume Object nodes, you must connect all the Volume Object nodes to a Composite node, and set this Composite node’s Mode property to Pass Through.
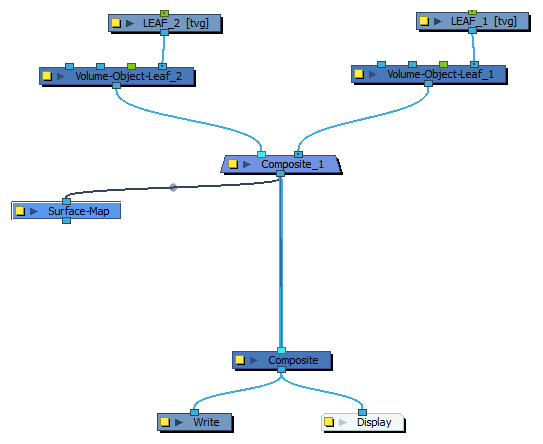

-
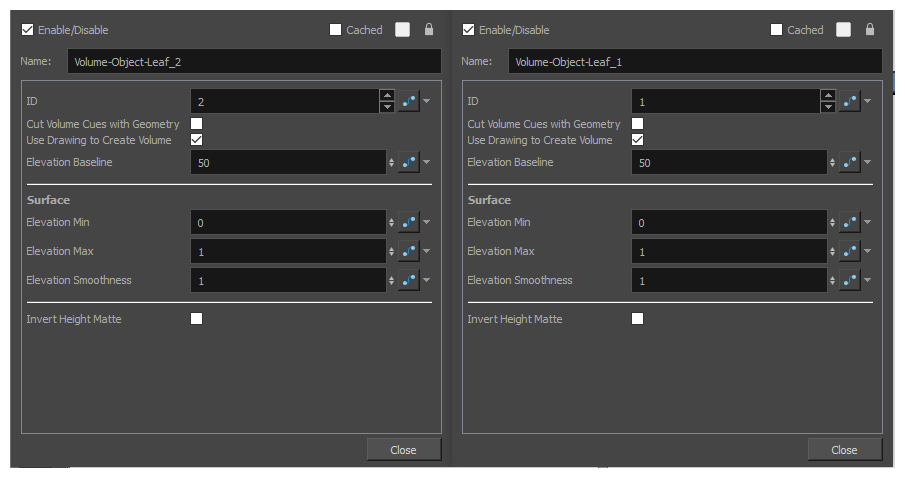
For each Volume Object node in your rig, click on their
 Layer Properties button to open their Layer Properties dialog, and set their ID parameter to different numbers.
Layer Properties button to open their Layer Properties dialog, and set their ID parameter to different numbers. For example, in this case, the ID of Volume-Object-Leaf_1 would be set to 1 and the ID of Volume-Object-Leaf_2 would be set to 2.
-
In the Node View, click the
 Layer Properties button of the Surface Map node to open its Layer Properties dialog.
Layer Properties button of the Surface Map node to open its Layer Properties dialog. -
In the Volume Creation section, add the Volume Objects you want to use to generate the surface map to the list below by doing one of the following:
- Open the Object drop-down and select each Volume Object you want to add to the list one by one.
- To add all the Volume Object nodes connected to the Surface Map node to the list, open the Object drop-down and select Add All Defined Objects.
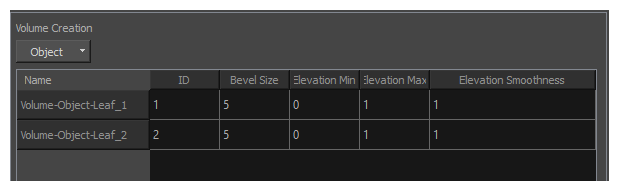
- For each Volume Object node in the list:
- Set the Elevation Min value to a value equal or higher than the Elevation Max value of the previous object. For the first object, this can be set to 0.
- Set the Elevation Max value to a value higher than the Elevation Min value for that object.
For example, if you have two Volume Objects, you can set the Elevation Min and Elevation max values for the first object to 0 and 1 respectively, and the Elevation Min and Elevation Max values for the second object to 1 and 2 respectively.
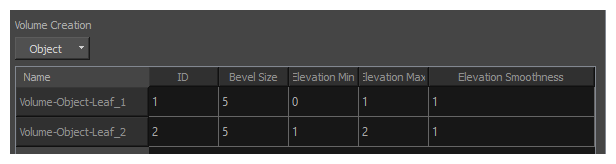 NOTES
NOTES- The Elevation Min and Elevation Max values for an object determine the range of space that each object occupies on the z-axis, and hence, how high each object is relative to other objects. This affects, among other things, how one object casts a shadow on other objects behind it.
- The Elevation Min parameter of an object should be equal or higher to the Elevation Max parameter of the previous object, so that volumes do not clip together.
- Elevation Min and Elevation Max parameters can have decimal values so as to lay different Volume Objects closer together.
- An object that is too elevated may end up behind the camera, which will cause the surface to be rendered with a hole in it.
To have a visual representation of your Surface Map as you configure the elevation of your objects, see Previewing the Surface Map.

-
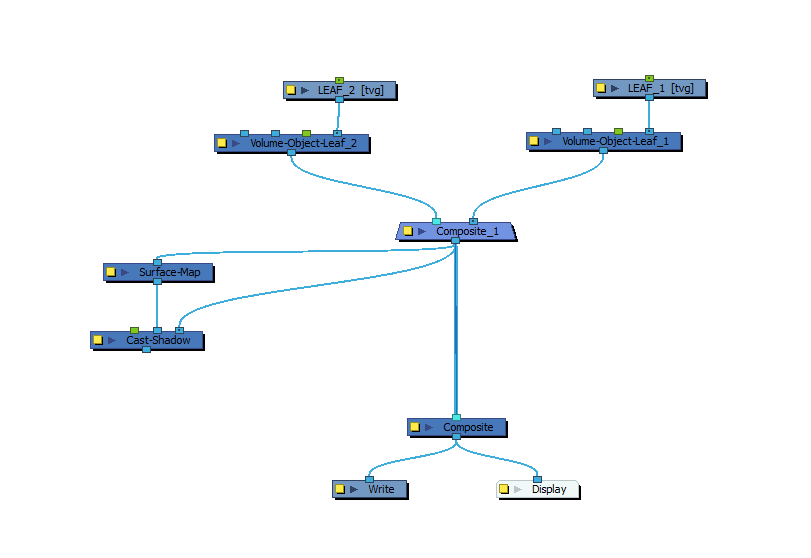
In the Node Library view, in the Shading category, select a Cast Shadow node and drag it to the Node View.
- Connect the output port of the Surface Map node to the middle input port of the Cast Shadow node.
-
Connect the output port of the Composite node combining your Volume Objects to the rightmost input port of the Cast Shadow node.
-
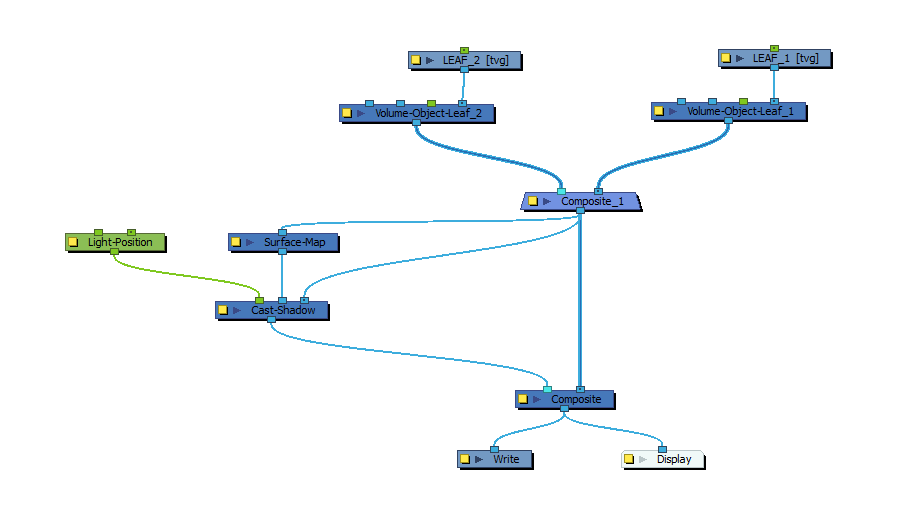
In the Node Library view, in the Shading category, select a Light Position node and drag it to the Node view. Then, connect the output port of the Light Position node to the leftmost (green) input port of the Cast Shadow node.

-
Connect the output port of the Cast Shadow node to the scene’s main Composite node, left of the port connecting that Composite node to the Composite that combines your Volume Object nodes. This will ensure that the shading effect is applied on top of the artwork.
-
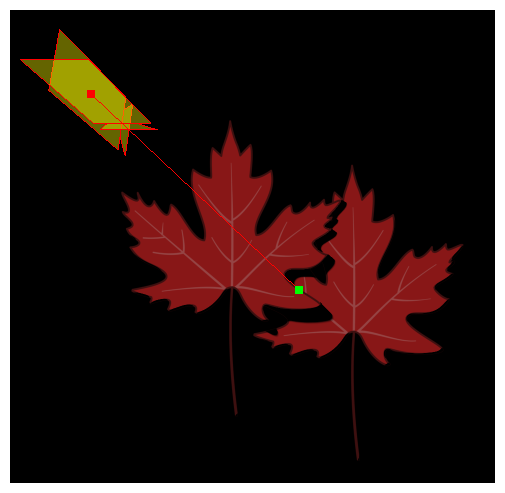
Position the Light Position node so that the object in the front casts a shadow onto the object in the back—see Positioning the Light Source for Surface Shading.

-
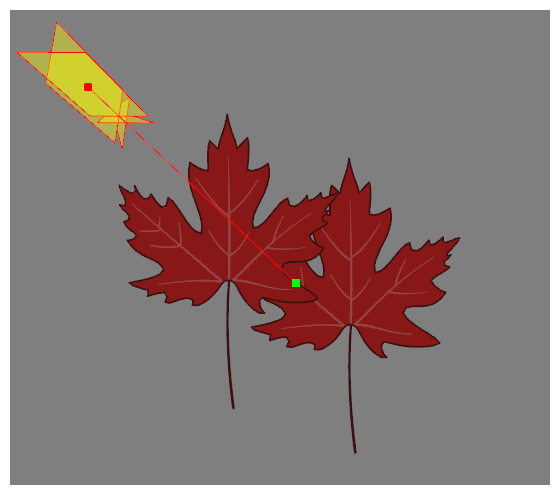
In the toolbar below the Camera view, click on the
Render View button to preview the cast shadow effect.
