Effect Stack View
The Effect Stack view is used to edit a sound clip by layering effects onto the clip. The parameters of these effects can be adjusted to fine tune the desired result. Pitch Shift, Reverb and Balance are a few examples of these effects.
- Do one of the following:
- In the Top menu, Select Windows > Effect Stack.
- In any view, click the Add View
button and select Effect Stack.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
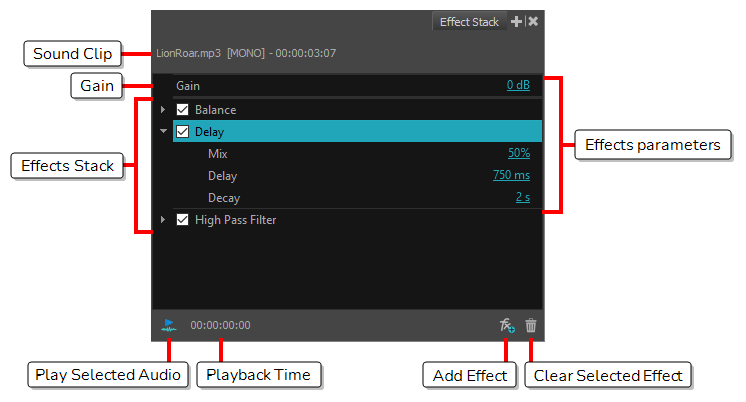
| Sound Clip |
Where the selected sound clip name is displayed. This includes the file name, file format and whether the file is mono or stereo (indicated in square brackets). The sound clip name is followed by the current time location of the playhead in the Timeline view. |
| Gain | A default effect in the Effect Stack with a decibel (dB) value of 0. Controls how loud the selected sound clip is before it goes through any processing (other effects are added). The gain value (loudness) can affect the tone of the sound clip as it goes through processing. |
| Effects Stack | Where effects are displayed. These effects can be disabled, enabled, have their parameter values modified or be deleted from the list. |
| Play Selected Audio | Click the Play Selected Audio button to playback the selected sound clip directly in the Effect Stack view. |
| Playback Time | Indicates the playback time location. |
| Add Effect | Click on the Add Effect button to display a list of sound effects that can be applied to the selected sound clip. Selecting an item from the list will add this effect to the bottom of the Effect Stack. |
|
Balance |
Applies volume independently to the left or right channel. Only works on clips with stereo sound. Mono audio clips will duplicate the audio in each channel and then apply the volume. |
|
Left Volume |
Sets the distribution of volume being applied to the left channel in decibels (dB). |
|
Right Volume |
Sets the distribution of volume being applied to the right channel in decibels (dB). |
|
Delay |
Applies an echo effect to the audio. |
|
Mix |
The percentage volume of the echo effect, as it is mixed with the original source audio. A value of 100% will only play the effect, whereas a value of 0% will only play the source audio. |
|
Delay |
Defines the delay between the original source audio and the initial echo reverberation, as well as between each subsequent reverberation. This value is in milliseconds (ms). |
|
Decay |
Defines the point at which the echoing source can no longer be heard. This value is in seconds (s). If there is more than one echo, each subsequent echo will get quieter and quieter over the length of the decay. Given a delay of 500 ms and a decay of 2 seconds (2000 ms), the listener will hear a total of 4 individual echos (2000 ms decay / 500 ms delay). |
|
High Pass Filter |
Passes frequencies higher than the Frequency Cutoff and mutes frequencies lower than the Frequency Cutoff. Will cut out all the bass of the audio clip and sounds tinnier. |
|
Frequency Cutoff |
Set point for passing frequencies above this value, while muting those below this point. Minimum = 0 hz (all frequencies pass), maximum = 22050 Hz (no frequencies pass). |
|
Low Pass Filter |
Passes frequencies lower than the Frequency Cutoff and mutes frequencies higher than the Frequency Cutoff. |
|
Frequency Cutoff |
Set point for passing frequencies below this value, while muting those above this point. Minimum = 0 hz (no frequencies pass), maximum = 22050 Hz (all frequencies pass). |
|
Pitch Shift |
Allows the pitch to be raised or lowered by a defined octave value. |
|
Pitch |
Sets the value in octaves by which to shift the pitch, where 0 octaves will result in the original audio. A positive value will increase the pitch, while a negative value will decrease the pitch. Octaves are on a logarithmic scale. This means that shifting the pitch up by one octave (+1) doubles the sound's frequency, while shifting the pitch down by one octave (-1) puts the sound at half its original frequency. |
|
Reverb |
Creates a reverberation effect that mimics the way sound bounces within an enclosed space. |
|
Mix |
The percentage volume of the reverberation effect, as it is mixed with the original source audio. A value of 100% will only play the effect, whereas a value of 0% will only play the source audio. |
|
Decay |
The time decay in seconds (s) for the length that an audio source reverberates within a space. A higher decay time sustains the reverberation for longer and produces more internal reverbs. A lower decay time results in a sharper reverberation. |
|
Absorb |
The amount as a percentage (%) that the reverberating audio is absorbed on each sample pass A lower absorption percentage allows the audio to endure for longer. A high absorption value muffles the reverberation faster. A 100% absorb value will result in no reverberation. |
|
Use Frequency Filter |
Determines whether the Reverb effect stifles frequencies outside a certain range. When this option is checked, the High Pass and Low Pass filters affect the sound clip's audio frequencies by their selected values. Without this option checked, frequencies will reverberate consistently. |
|
Low Pass |
When the Use Frequency Filter option is enabled, this value defines what frequencies can pass on each reverberation. Frequencies below this value will be audible, but frequencies above it will be muted. This parameter can be adjusted to create hollower sounding rooms and larger spaces. |
|
High Pass |
When the Use Frequency Filter option is enabled, this value defines what frequencies can pass on each reverberation. Frequencies above this value will be audible, but frequencies below it will be muted. This parameter can be adjusted to create bouncier sounding rooms with harder walls. |
|
Volume |
Controls how loud the sound clip is after it’s been processed. |
|
Volume |
Increase the decibel (dB) value to a number greater than 0 to increase the loudness of the selected sound clip or to a value less than 0 to decrease loudness, where 0 is the starting value. Unlike gain, the volume's loudness will not affect the tone of the sound. The Volume range is -96 dB to +6 dB. |
| Clear Selected Effect | After selecting an effect from the Effect Stack, click on this button to delete the effect from the stack. |