The Three-Points Constraint translates, rotates and scales a drawing to make it follow the pivots of the three pegs connected to it.
Connection
The Three-Points Constraint node must be connected to three Peg nodes. The pivot point of each peg will define the resting position of one of the points used to transform the drawing connected under it. When one of the pegs is moved, the Three-Points Constraint will transform the drawing so that it follows the pivot point of that peg.
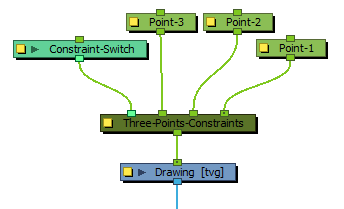
Optionally, the leftmost input port of a Three-Points Constraint node can be connected to a Constraint-Switch, which can be used to reduce the effect of the Three-Points Constraint node on the element it is connected by setting its Active parameter between 0 and 100.
Controls
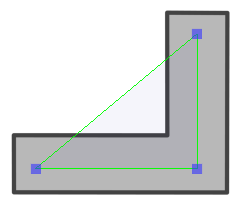
When the controls of the Three-Points Constraint are displayed, the position of the three points are displayed with blue squares linked by a green line.
These points are only a visual representation and cannot be manipulated.
- In the Tools toolbar, select the Transform tool or press Shift + T.
- Do one of the following:
- Select one of the pegs the Three-Points Constraint is connected to, then move the peg by clicking and dragging the centre point in the Camera view.
- In the layer properties of the element, disable the Animate Using Animation Tools option. Then, select the element, and click and drag the element near one of the points. The point that is the closest to the mouse cursor will be automatically selected and moved.
Properties
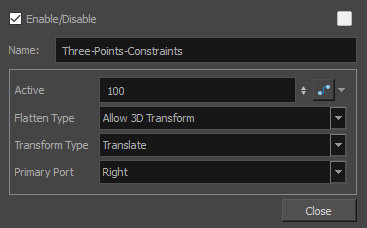
| Parameter | Description |
| Active |
The percentage of influence the constraint has on its child element. If set to 100, the element will follow the three points closely. If set to 0, the element will not be affected by the constraint. If a Transformation Switch node is connected to the Three-Points Constraint node, the Active parameters of the Transformation Switch and the Three-Points Constraint nodes will be multiplied together. |
| Flatten Type |
This parameter defines what happens if one of the pegs defining the constraint points is moved on the Z-axis:
NOTE This projection is based on the position of the primary point peg on the Z-axis. Hence, if the three pegs are on a different position on the Z-axis, there may be a perceived offset between the position of the non-primary points and their effect on the element.
|
| Transform Type |
By default, only the position of the points is used to transform the element. Since those points are defined by pegs, these pegs can also be subjected to scale, angle and skew transformations that would be normally ignored by the Three-Points Constraint node. This parameter can be used to apply the other transformations done on the peg of the primary point on the element, rather than ignoring them.
|
| Primary Port |
Defines which one of the ports, and hence, which one of the pegs the node is connected to, is used to define the primary point. The primary point affects the other parameters in the following ways:
|