Traditional Animation Workflow
In a traditional workflow, many steps are done manually. Harmony is used for the digital portion. We will focus mainly on these steps.
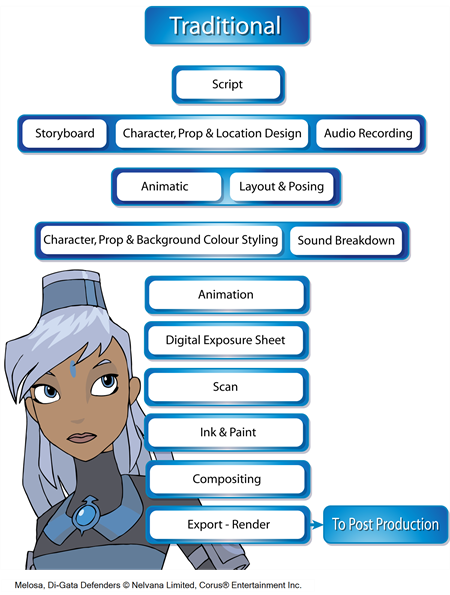
The following is a list of the steps done using Harmony in a traditional animation workflow. This will help you understand how the work is divided and give you a base to start building your own traditional pipeline.
The layout and posing process links the storyboard artist and the animator. The layout artist uses the storyboard and prepares an organized folder for the animator. This folder contains a field guide that shows the proper camera move and the right size of the scene. It also includes the character's main poses from the storyboard following the official design, and the effects, backgrounds and all the other information necessary to the animator.
The backgrounds are done directly out of the storyboard and location design. A background is a section or an angle of a location. The background artist refers to the storyboard and draws the background for each scene. Once the background is completed, it is added to the layout folder.
In a cut-out or paperless animation process, this step can be done digitally or traditionally. This will depend on the user's preferences.This step is mainly applied to larger productions. An individual user can move directly from the storyboard to the animation.
This step can be done with Harmony, but Toon Boom also has another software developed for this. Toon Boom Storyboard Pro has optimized tools to create the layout and posing.
Traditional animation is done on paper. The animator receives the layout folder and uses the references to animate the scene. The animator will draw each frame of the animation or each pose of the character. If there is dialogue in the scene, the animator will follow the breakdown and animate the mouths and expressions.
Depending on the studio size, the animation can be divided in different ways. Sometimes the animator will do all of the work, from the key poses to the in-betweens and then the clean up. Bigger studios will have the animator doing only the key poses and then send the scene to the in-between department and finally to the clean up department.
Once the animation is completed, it is sent to the digital part of the process. This applies only to modern processes. In the traditional, old-fashioned pipeline, the animation was sent for hand-inking and painting. The animation was traced with ink on transparent cels and the colours are painted with brushes on the other side of the cel to fill the zones. Today, using Harmony, you can still use this technique by utilizing the digital Line Art and Colour Art feature.
The digital exposure sheet is the first step done in Harmony. This controls the timing of the animation. The traditional animator creates a paper exposure sheet in order to create the timing. The person in charge of the digital exposure sheet reads the paper version and recreates it in Harmony. Once the drawings are all in place on the exposure sheet, the scene is ready for the scan.
Note that a single user will scan the drawings first and then set the timing in the exposure sheet. The digital exposure sheet is only created first in a larger animation studio using the advanced scan features available in Harmony.
Scanning is the second step in Harmony. The cleaned-up drawings are scanned and imported in the software in a simple step that incorporates all of the drawings in the scene. When all the drawings are scanned, they are ready to be inked and painted (coloured in).
At this point in the process, the colour models are ready and the drawings are scanned in and properly exposed. Using Harmony's optimized tools, the colourist can clean the scanned artwork and start applying colour to the different drawings. When the drawings are cleaned, as well as inked and painted, they are ready for compositing.
The compositor imports the coloured background, animatic reference and sound as required. Referring to the exposure sheet, animatic and animation, the compositor assembles all these elements and creates the camera moves and other necessary motions. Finally, the compositor adds any digital effects required by the scene. These can include tones, highlights and shadows. When the compositing is completed, the final step is the rendering.
Once the compositing is completed, the last step is to render the scene as a movie or an image sequence. Generally, the compositor will be the same person doing the render.